Documentation setup
The documentation for Dareplane is generated with Quarto and quartodoc. The later is used to automatically generate API documentation for python modules. quarto uses a central _quarto.yml file to configure the documentation.
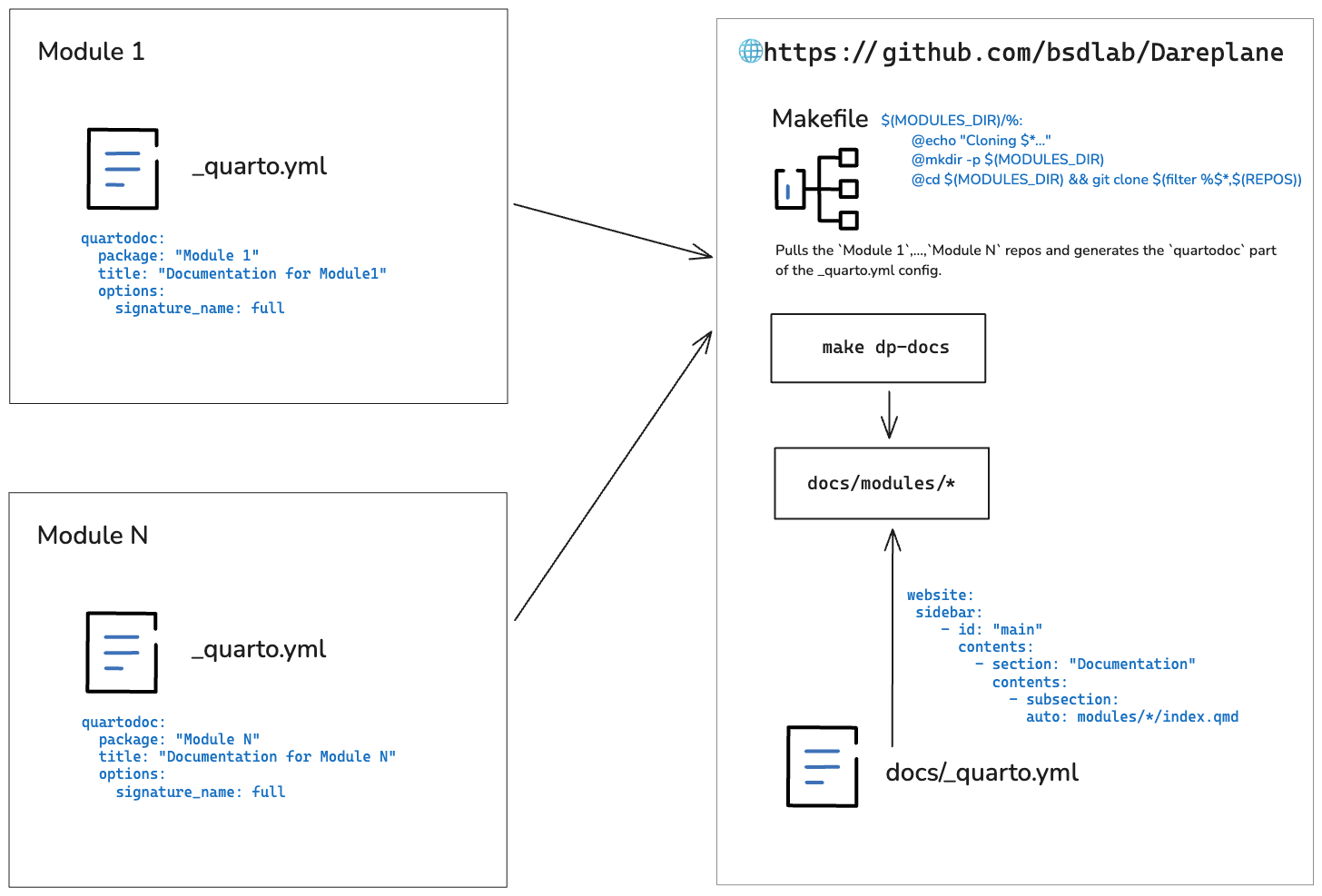
For the Dareplane documentation, https://github.com/bsdlab/Dareplane is the main repository, and the /docs folder therein should be considered the root for all quarto related steps.
Schematic of the generation process
Run the documentation build locally
To run the docs building for all modules, clone https://github.com/bsdlab/Dareplane and cd docs.
In the build across multiple modules, the Makefile has the following build steps defined:
- generate the
main.qmddynamically from theREADME.md - extract the repositories from the first table in the
main.qmd, taking the first column and expecting markdown notation for links - download each repository into a
/docs/modules/*directory - build with
quartodoc buildwithin each/docs/modules/*folder
To create a fresh build, execute the following:
make cleanmake main # copy README -> main.qmdmake modules.csv # extract the reposmake docs-gallery # build the docs within each moduleOnce the quartodoc part in each /docs/modules/* is done (make docs-gallery), we can use quartop preview (or the github publish action for Dareplane) to build the quarto website from within /docs for Dareplane. All modules will be included as we can specify a Documentation subsection with a glob in _quarto.yml:
website:
sidebar:
- id: "main"
contents:
- section: "Documentation"
contents:
- subsection:
auto: modules/*/index.qmdHow to document your module
In harmony with the general Dareplane coding philosophy, we want every module to be standalone, with very limited requirements for interoperability. This also holds for the documentation. The only requirement for the automated documentation process to be able to pick up the documentation is that there exists a _quarto.yml file in the root directory, which contains a least a section for quartodoc. E.g.:
quartodoc:
package: "dp-control-room"
source_dir: "control_room" # should point the the folder containing the python code
title: "Documentation control room"With this setup, you can first create your documentation on a per module level, making sure it works with quartodoc build. The quartodoc build command will use doc-strings of the python functions and classes to dynamically create markdown documentation pages.
For debugging, it might be handy to add a general quarto website section on the per module _quarto.yml file. See the Single module quarto section for an example.
This can be done without interference with the generation on the across modules documentation, as the latter is only using the quartodoc part.
Single module quarto
This section provides an example of how we would document a single Dareplane module.
Let us assume we are documenting the dp-stroop module.
Initial _quarto.yml
Start out by creating the _quarto.yml file, containing a quartodoc section with an entry for the run_paradigm_cli function:
quartodoc:
package: "dp-stroop" # name of the package
source_dir: "stroop_task" # as the source code is within this folder
title: "Documentation for the Stroop task"
options:
signature_name: full
# write sidebar where quartodoc writes its content without impacting quarto
sidebar:
file: "_stroop_sidebar.yml"
sections:
- title: "The Stroop task"
desc: |
:::{.callout-info}
The github repository for this module is located at:
[https://github.com/bsdlab/dp-stroop](https://github.com/bsdlab/dp-stroop)
:::
- subtitle: Modified Stroop task
package: stroop_task
desc: The main script to start the Stroop task from command line.
contents:
- main.run_paradigm_cliBuild the documentation
Now we can build the documentation with quartodoc build. This will create a ./reference folder with the documentation.
Add the ./reference folder and objects.json to the .gitignore to avoid cluttering of the repo. Docs will be generated dynamically.
echo reference/ >> .gitignore
echo objects.json >> .gitignore
echo _site/ >> .gitignore # will be created from `quarto preview` see next stepAdd a standalone website section
With having the quartodoc section in the _quarto.yml, we already have everything we need, but it is hard validate that the documentation builds as intended. The most straight forward solution is to add a website section to the _quarto.yml, which then allow to debug with quarto preview:
project:
type: website
website:
sidebar:
- id: "main"
contents:
- section: "Documentation"
contents:
- reference/index.qmd
metadata-files:
- reference/_stroop_sidebar.ymlThen run:
quarto previewThis will open a browser window with the documentation.
Continue adding more content
Now it is up to adding more sections to the documentation, which can be done by enriching the contents: of the quartodoc section in the _quarto.yml.
contents:
- main.run_paradigm_cli
- context.StroopContextNote:
While the quarto part will update dynamically (hot reloading), quartodoc will need to be recompiled every time you add to the
quartodocsection of the_quarto.yml.The
quarto previewmight spawn not at the root of the created website but on a specific functions/classed documentation page. Simply prune the path in the browser to get to the root. E.g., fromhttp://localhost:6901/reference/main.run_paradigm_cli.htmltohttp://localhost:6901/quartodocwill add documentation for methods from each method’s own doc string. Avoid having amethodsdoc string section on the class wide doc string as this will lead to aNotImplementedErrorfromgriffe.